
Cybersecurity is a vital aspect of any organization’s operations, especially in the digital age. Cyberattacks can cause significant damage to the reputation, finances, and productivity of businesses, as well as compromise the privacy and security of their customers and employees. A cybersecurity framework is a set of guidelines, standards, and best practices that provide a common language and approach for managing cybersecurity risks. There are many cybersecurity frameworks available, each with its own scope, objectives, and benefits. Depending on the industry, size, and needs of the organization, different frameworks may be more suitable or applicable than others. In this article, we will introduce seven of the most popular and widely used cybersecurity frameworks that can help reduce cyber risk.
1. NIST Cybersecurity Framework
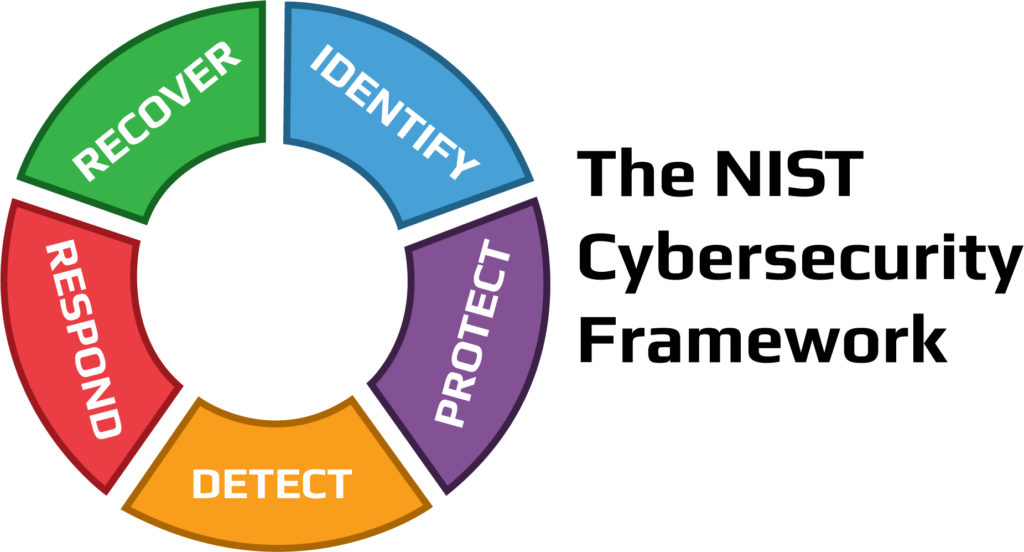
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework Standards (NIST CSF) was developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), a U.S. federal agency, in response to an executive order by former President Obama in 2014. The NIST CSF aims to provide a voluntary and flexible guidance for organizations to improve their cybersecurity, especially for those in the critical infrastructure sectors, such as energy, transportation, and healthcare. The NIST CSF has five primary functions: identify, protect, detect, respond, and recover. The NIST CSF is widely adopted and recognized as a leading cybersecurity framework, both in the U.S. and internationally. It is compatible with other standards and regulations, such as ISO 27001, SOC2, HIPAA, and GDPR. It also offers various resources and tools, such as quick-start guides, success stories, and a searchable catalog, to facilitate its implementation and adoption.
Learn more about: Cybersecurity services in Houston
2. ISO 27001 and ISO 27002
ISO 27001 and ISO 27002 are international standards for information security management systems (ISMS) developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). They provide a systematic and comprehensive approach for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and improving the security of information assets within an organization. It covers 14 domains, such as security policies, access control, cryptography, and incident management, and provides guidelines and recommendations for selecting and applying appropriate security measures.

ISO 27001 and ISO 27002 are widely recognized and respected as global standards for information security. They also help organizations comply with other regulations and frameworks, such as GDPR, NIST CSF, and SOC2. Moreover, they enable organizations to obtain an independent certification that demonstrates their adherence to the standards and their commitment to information security.
3. SOC2
In cybersecurity frameworks comparison SOC2 is also a framework for reporting on the controls and practices related to the security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy of a service organization’s systems. It was developed by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) and is based on the Trust Services Criteria (TSC). SOC2 reports are also useful for service organizations to evaluate and improve their internal controls and processes. SOC2 reports are classified into two types: Type 1 and Type 2. A Type 1 report describes the design and implementation of the service organization’s controls and practices as of a specific date. SOC2 reports are also aligned with other standards and frameworks, such as ISO 27001, NIST CSF, and HIPAA.

4. NERC-CIP
NERC-CIP is a set of standards and requirements for the protection of the bulk electric system (BES) in North America. It was developed by the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC), a non-profit organization that oversees the reliability and security of the BES, and is enforced by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC), a U.S. A federal agency that oversees the transmission and sale of energy. NERC-CIP also requires entities that own, operate, or use the BES to conduct regular assessments, audits, and tests to ensure compliance and performance.

NERC-CIP is mandatory and legally enforceable for all entities that are part of the BES, such as electric utilities, generators, transmission operators, and service providers. NERC-CIP also helps entities comply with other regulations and frameworks, such as NIST CSF, HIPAA, and FISMA. Moreover, NERC-CIP promotes the resilience and security of the BES, which is essential for the safety and well-being of the public and the economy.
5. HIPAA
HIPAA is a U.S. federal law that sets the standards and rules for the protection of the privacy and security of health information. It was enacted in 1996 and is administered by the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) and the Office for Civil Rights (OCR). HIPAA consists of several rules and provisions, such as the Privacy Rule, the Security Rule, the Breach Notification Rule, and the Enforcement Rule. The Privacy Rule establishes the rights and obligations of individuals and entities regarding the use and disclosure of protected health information (PHI).

Health care providers, health plans, and health care clearinghouses are all examples of covered entities. Business associates include any entity that performs functions or activities on behalf of a covered entity that involve access to PHI or e-PHI, such as billing services, cloud service providers, and consultants. HIPAA also helps entities comply with other regulations and frameworks, such as NIST CSF, ISO 27001, and GDPR.
6. GDPR
GDPR is a regulation that governs the protection of the personal data of individuals in the European Union (EU) and the European Economic Area (EEA). It was adopted in 2016 and became effective in 2018. It is considered one of the most comprehensive and stringent data protection laws in the world. GDPR defines personal data as any information that relates to an identified or identifiable natural person, such as name, email, location, biometric data, or online identifiers.

GDPR grants individuals various rights and controls over their personal data, such as the right to access, rectify, erase, restrict, port, and object to the processing of their data. GDPR also imposes various obligations and responsibilities on entities that collect, process, or store personal data, such as the duty to obtain consent, provide transparency, implement security measures, conduct data protection impact assessments, establish data protection officers, and notify any data breaches. GDPR also helps entities comply with other regulations and frameworks, such as NIST CSF, ISO 27001, and HIPAA.
See related: Our Managed IT services
7. FISMA
FISMA is a U.S. federal law that establishes the requirements and standards for the security of information systems and data that support the operations and assets of federal agencies. It was enacted in 2002 and is administered by the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) and NIST.
FISMA requires federal agencies to implement an information security program that covers the planning, development, implementation, evaluation, and improvement of the security of their information systems and data. FISMA also requires federal agencies to conduct regular risk assessments, audits, and reports.

Conclusion
Cybersecurity frameworks are critical tools for firms to manage and reduce cyber threats. They provide a common language and approach for identifying, protecting, detecting, responding to, and recovering from cyber threats. In this article, we have introduced seven of the most popular and widely used cybersecurity frameworks: NIST CSF, ISO 27001 and ISO 27002, SOC2, NERC-CIP, HIPAA, GDPR, and FISMA. Each framework has its own scope, objectives, and benefits, and can be applied to different types of organizations and industries. By choosing and implementing the most suitable framework for their needs, organizations can improve their security posture, comply with relevant regulations, and demonstrate their commitment to cybersecurity to their stakeholders. Therefore, organizations should always keep up with the latest developments and best practices in the field of cybersecurity and adopt a proactive and adaptive mindset.


