Zero trust is a security framework that assumes no user, device, or network is trustworthy by default, and requires continuous verification and authorization for every access request. Zero trust aims to protect sensitive data and assets from unauthorized access, breaches, and cyber-attacks, by minimizing the attack surface and reducing the risk of lateral movement.
Zero trust is not a product or a tool, but a mindset and a strategy that can be applied to any organization, regardless of its size, industry, or infrastructure. However, implementing zero trust can be challenging, as it requires a shift in culture, processes, and technologies. In this article, we will outline some of the benefits, principles, and steps of implementing a zero trust security model in your organization.
Benefits of Zero Trust
Zero trust can offer several benefits for your organization, such as:
- Enhanced security: By verifying every access request and enforcing granular policies, zero trust can prevent unauthorized access, data leakage, and malware infection, and help you comply with regulatory standards and best practices.
- Improved visibility: By collecting and analyzing data from every access point, zero trust can provide you with a comprehensive view of your network activity, user behavior, and security posture, and help you identify and respond to threats faster and more effectively.
- Increased efficiency: By automating and streamlining the verification and authorization processes, zero trust can reduce the complexity and overhead of managing multiple security solutions, and improve the user experience and productivity.
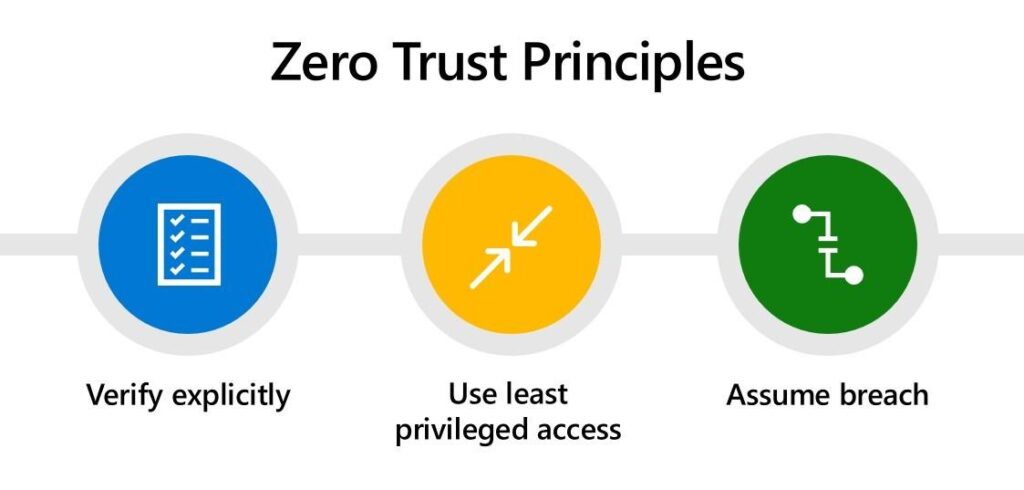
Principles of Zero Trust
Zero trust is based on a set of principles that guide the design and implementation of the security framework. These principles are:
Verify explicitly:
Every user, device, and network connection should be verified before granting access, regardless of their location, role, or status. Verification should be based on multiple factors, such as identity, context, device health, and risk level.
Enforce least privilege:
Every user, device, and network connection should be granted the minimum level of access required to perform their tasks, and nothing more. Access should be revoked or modified as soon as the user, device, or network changes or the task is completed.
Assume breach:
Every user, device, and network connection should be treated as a potential threat, and monitored and audited for any suspicious or anomalous activity. Any sign of compromise should trigger an immediate response and remediation.
Steps to Implement Zero Trust
Implementing zero trust is not a one-time project, but a continuous journey that requires planning, execution, and improvement. Here are some of the steps you can take to implement zero trust in your organization:
Identify sensitive data and assets:
Start by identifying where your critical data resides and the digital assets requiring the highest protection levels. Understanding what needs to be protected is crucial for effectively applying the zero trust principles.
Map the transaction flows:
Understand how data moves across your organization, and who accesses it, when, where, why, and how. This will help you define the boundaries and segments of your network, and the policies and controls that govern them.
Architect your zero trust networks:
Design your network architecture based on the zero trust principles, and use technologies such as micro-segmentation, identity-aware proxies, and software-defined perimeters to isolate and protect your sensitive data and assets. You should also encrypt your data at rest and in transit, and use secure protocols and certificates for communication.
Monitor and maintain security:
Monitor and analyze your network activity, user behavior, and security posture, and use real-time alerts and dashboards to detect and respond to threats. You should also conduct regular audits and reviews of your security policies and controls, and update them as needed.
Continuous improvement:
Implementing zero trust is not a static process, but a dynamic one that requires constant evaluation and adaptation. You should always seek feedback from your stakeholders, measure your performance and outcomes, and look for ways to improve your security framework and align it with your business goals and needs.
Zero Trust Technologies and Solutions
To implement a zero trust security model, you need to use various technologies and solutions that can help you verify and authorize every access request, enforce granular policies, encrypt and protect your data, and monitor and respond to threats. Some of the common zero trust technologies and solutions are:
Micro-segmentation:
This is a technique that divides your network into smaller and isolated segments, each with its own security policies and controls. Micro-segmentation can help you reduce the attack surface, limit the lateral movement of attackers, and isolate and contain breaches.
Identity-aware proxies:
These are services that act as intermediaries between users and applications, and provide secure and context-aware access to them. Identity-aware proxies can help you verify the identity and context of users, enforce multi-factor authentication, and apply adaptive policies based on risk level.
Identity and access management:
This is a system that manages the identities and access rights of users and devices, and provides secure and seamless authentication and authorization. Identity and access management can help you verify the identity and device health of users, grant granular and dynamic access rights, and revoke or modify access as needed.
Data encryption:
This is a process that transforms data into an unreadable format, using a secret key or algorithm, and prevents unauthorized access or modification. Data encryption can help you protect your data at rest and in transit, and ensure its confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Security monitoring and analytics:
This is a system that collects and analyzes data from various sources, such as logs, events, alerts, and dashboards, and provides visibility and insight into your network activity, user behavior, and security posture. Security monitoring and analytics can help you detect and respond to threats, identify and remediate vulnerabilities, and improve your security performance and outcomes.
Zero Trust Best Practices and Tips
To implement a zero trust security model successfully, you need to follow some best practices and tips that can help you design and deploy your security framework effectively and efficiently. Some of the best tips and practices are:
Start small and scale up:
Implementing zero trust can be a complex and challenging process, and it may not be feasible or advisable to do it all at once. Then, you can gradually expand your scope and scale up your zero trust security model, based on your needs and priorities.
Align with your business goals and needs:
Implementing zero trust is not a one-size-fits-all solution, but a customized and tailored one that should suit your organization’s specific context and requirements. Therefore, you should align your zero trust security model with your business goals and needs, such as your industry, size, infrastructure, regulations, and risk appetite, and design and deploy your security framework accordingly.
Leverage existing tools and solutions:
Implementing zero trust does not necessarily mean that you have to replace or discard your existing tools and solutions, but rather that you can leverage and integrate them with your zero trust security model By leveraging existing tools and solutions, you can save time, money, and effort, and optimize your security resources and capabilities.
Conclusion
Zero trust is a security framework that can help you protect your organization from unauthorized access, breaches, and cyberattacks, by verifying and authorizing every access request and enforcing granular policies. Implementing zero trust can be challenging, but also rewarding, as it can enhance your security, visibility, and efficiency. By partnering with Uprite Services IT Company, you’ll gain access to cutting-edge security solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our team of experts will guide you through every step of the Zero Trust implementation process, ensuring that your organization remains resilient against unauthorized access and cyber-attacks. For more information and guidance on how to conduct cybersecurity risk assessment, you can check out these resources.